Nerve Regeneration
ABOUT
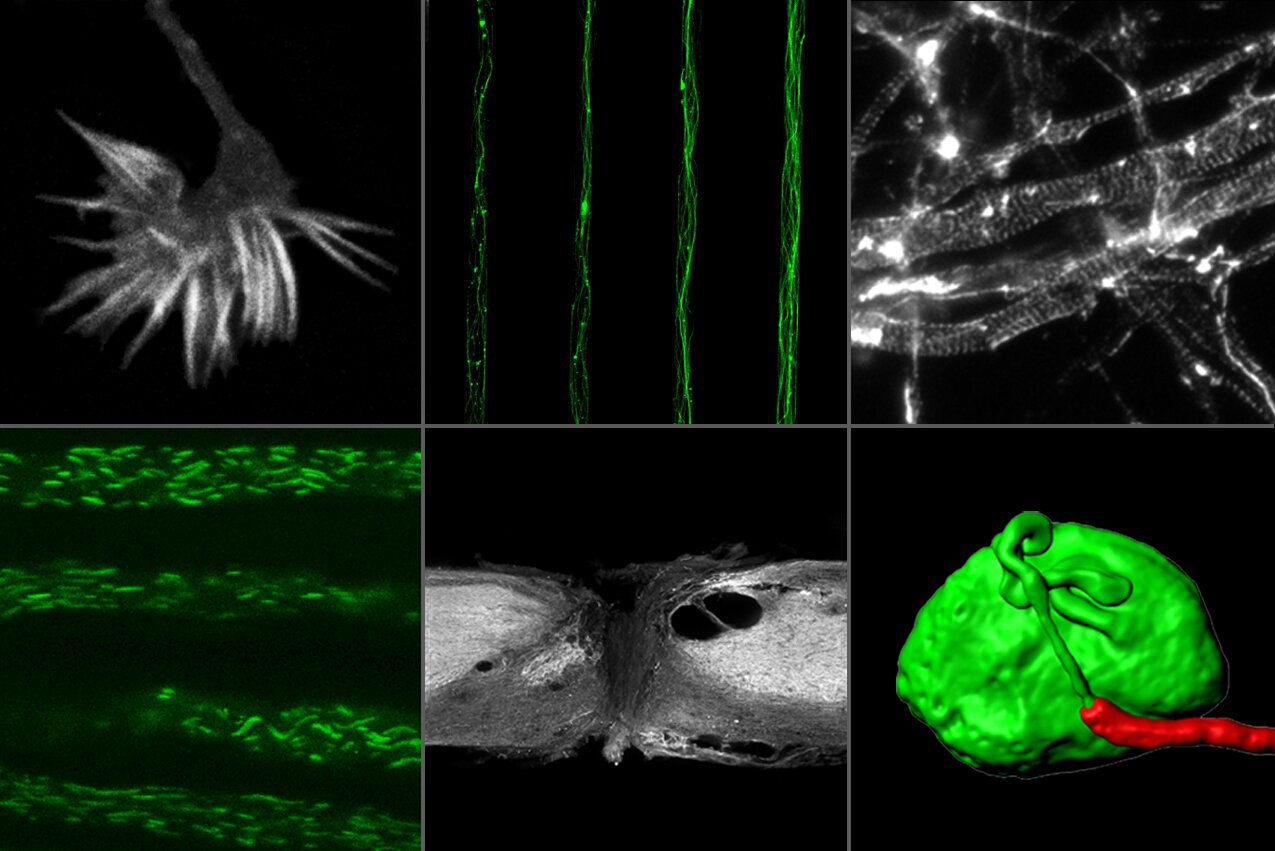
We are interested in characterising pathways that control axon growth during development, and axon degeneration and regeneration following injury and disease. We have a special focus on studying the axonal cytoskeleton organisation and dynamics, and axonal trafficking.
RESEARCH
Neurons, one of the most striking examples of polarization in eukaryotic cells, are dependent on cytoskeleton dynamics and trafficking to establish their distinctive cell shape and function. Understanding the basic neuronal cell biology is crucial to unraveling the causes of neurodegeneration, and to developing strategies to promote axon regeneration.
Research in our group has currently the following main topics:
- Characterize the biogenesis and function of the axonal membrane periodic skeleton;
- Identify determinants of the central-peripheral polarity of dorsal root ganglia neurons;
- Understand cytoskeleton dynamics and trafficking during axon (re)growth and degeneration;
- Understand the mechanisms allowing the spiny mouse to spontaneously regenerate the CNS.
Our work brings together in vitro neuronal cell culture systems, microfluidics, and in vivo rodent models, including the model of spinal cord injury and models of rare neurodegenerative disorders (Globoid Cell Leukodystrophy and Amyloid-related neuropathies). These models combined with genetic strategies, cell biology and biochemical approaches, and state-of-the-art microscopy, allow us to advance our knowledge on the mechanisms that regulate axon growth, degeneration and regeneration.
Team
Selected Publications
Neurons contribute to pathology in a mouse model of Krabbe disease in a cellautonomous manner. PLoS Biology20(7):, 2022. [Journal: Article] [CI: 1] [IF: 9,8]
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001706 SCOPUS: 85134360903
Nascimento A.I., Da Silva T.F., Fernandes E.C., Luz L.L., Mar F.M., Safronov B.V., Sousa M.M.,
Sensory neurons have an axon initial segment that initiates spontaneous activity in neuropathic pain. Brain145(5):1632-1640, 2022. [Journal: Article] [CI: 7] [IF: 14,5]
DOI: 10.1093/brain/awac078 SCOPUS: 85131702538
Nogueira-Rodrigues J., Leite S.C., Pinto-Costa R., Sousa S.C., Luz L.L., Sintra M.A., Oliveira R., Monteiro A.C., Pinheiro G.G., Vitorino M., Silva J.A., Simão S., Fernandes V.E., Provazník J., Benes V., Cruz C.D., Safronov B.V., Magalhães A., Reis C.A., Vieira J., Vieira C.P., Tiscórnia G., Araújo I.M., Sousa M.M.,
Rewired glycosylation activity promotes scarless regeneration and functional recovery in spiny mice after complete spinal cord transection. Developmental Cell57(4):440-450.e7, 2022. [Journal: Article] [CI: 19] [IF: 11,8]
DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.12.008 SCOPUS: 85123830565
Pinto-Costa R., Sousa S.C., Leite S.C., Nogueira-Rodrigues J., da Silva T.F., Machado D., Marques J., Costa A.C., Liz M.A., Bartolini F., Brites P., Costell M., Fässler R., Sousa M.M.,
Profilin 1 delivery tunes cytoskeletal dynamics toward CNS axon regeneration. Journal of Clinical Investigation130(4):2024-2040, 2020. [Journal: Article] [CI: 20] [IF: 14,8]
DOI: 10.1172/JCI125771 SCOPUS: 85082814702
Costa A.R., Sousa S.C., Pinto-Costa R., Mateus J.C., Lopes C.D.F., Costa A.C., Rosa D., Machado D., Pajuelo L., Wang X., Zhou F.Q., Pereira A.J., Sampaio P., Rubinstein B.Y., Pinto I.M., Lampe M., Aguiar P., Sousa M.M.,
The membrane periodic skeleton is an actomyosin network that regulates axonal diameter and conduction. eLife9:, 2020. [Journal: Article] [CI: 37] [IF: 8,1]
DOI: 10.7554/eLife.55471 SCOPUS: 85082635132
Nascimento A.I., Mar F.M., Sousa M.M.,
The intriguing nature of dorsal root ganglion neurons: Linking structure with polarity and function. Progress in Neurobiology168:86-103, 2018. [Journal: Review] [CI: 69] [IF: 10,7]
DOI: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2018.05.002 SCOPUS: 85048777484
Leite S.C., Sampaio P., Sousa V.F., Nogueira-Rodrigues J., Pinto-Costa R., Peters L.L., Brites P., Sousa M.M.,
The Actin-Binding Protein a-Adducin Is Required for Maintaining Axon Diameter. Cell Reports15(3):490-498, 2016. [Journal: Article] [CI: 76] [IF: 8,3]
DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.03.047 SCOPUS: 84962762309