Structural Biochemistry
ABOUT
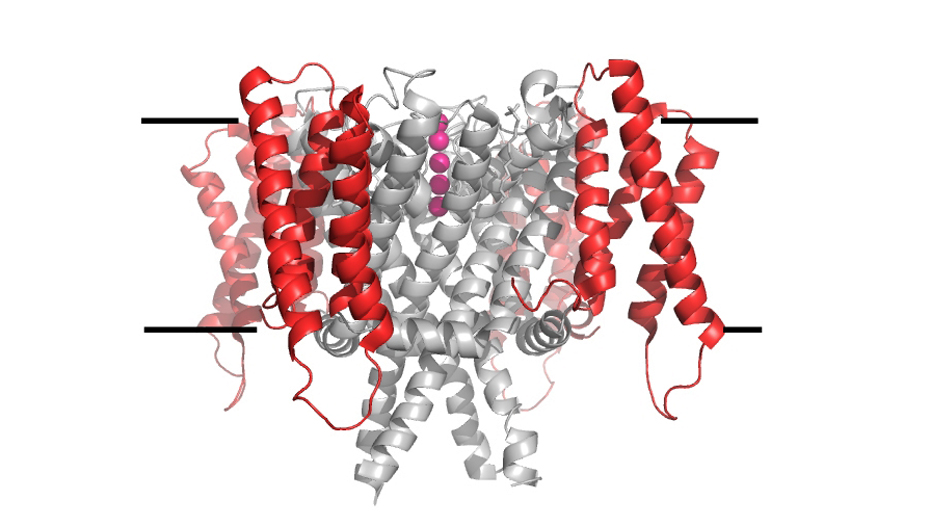
We are generally interested on the mechanisms of ion transport across the cell membrane. We have two active research lines, the characterization of the molecular properties of KCNH channels, a family of eukaryotic K+ channels, and the study of the mechanisms that regulate the intracellular concentration of potassium ion in bacteria.
RESEARCH
KCNH channels: KCNH channels have important roles in neuronal excitability, cardiac repolarization and cell proliferation. The human ERG (hERG) K+ channel conducts a cardiac repolarizing current and mutations or channel block cause long QT syndrome (LQTS) and catastrophic ventricular arrhythmias. We have developed single-chain antibody fragments (scFv) that bind to the intracellular PAS domain of the hERG channel and modulate its functional properties. These studies suggest that the interactions established by the PAS domain with the rest of the channel are dynamic, changing with the functional states of the channel. Moreover, the scFv molecules increased the amount of current conducted by hERG and shortened the Action Potential Duration in cardiomyocytes, demonstrating therapeutic potential. We are now using these molecules to explore the mechanism of hERG activation.
Regulation of intracellular K+ in bacteria: All organisms on Earth accumulate large amounts of K+ inside the cell. In bacteria, intracellular K+ has a role in determining intracellular pressure (turgor), pH and membrane potential. In addition, regulation of intracellular K+ is essential for bacteria to adapt to extracellular changes. Our studies are focused in understanding the molecular properties of K+ transporters that mediate inward and outward ion movement and how these opposing activities are balanced to allow a controlled amount of K+ inside the cell. This fundamental understanding is crucial to define if these transporter systems are potential candidates for anti-microbial strategies.
Team
Selected Publications
c-di-AMP determines the hierarchical organization of bacterial RCK proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America121(18):, 2024. [Journal: Article] [CI: 2] [IF: 9.1]
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2318666121 SCOPUS: 85191240397
Stevens-Sostre W.A., Flores-Aldama L., Bustos D., Li J., Morais-Cabral J.H., Delemotte L., Robertson G.A.
An intracellular hydrophobic nexus critical for hERG1 channel slow deactivation. Biophysical Journal123(14):2024-2037, 2024. [Journal: Article] [CI: 3] [IF: 3.1]
DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.01.010 SCOPUS: 85184778601
Harley C.A., Bernardo-Seisdedos G., Stevens-Sostre W.A., Jones D.K., Azevedo M.M., Sampaio P., Lorga-Gomes M., Trudeau M.C., Millet O., Robertson G.A., Morais-Cabral J.H.
Conformation-sensitive antibody reveals an altered cytosolic PAS/CNBh assembly during hERG channel gating. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America118(44):, 2021. [Journal: Article] [CI: 9] [IF: 12,8]
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2108796118 SCOPUS: 85119299559
Cereija T.B., Guerra J.P.L., Jorge J.M.P., Morais-Cabral J.H.
c-di-AMP, a likely master regulator of bacterial K+ homeostasis machinery, activates a K+ exporter. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America118(14):, 2021. [Journal: Article] [CI: 30] [IF: 12,8]
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2020653118 SCOPUS: 85103744229
Teixeira-Duarte C.M., Fonseca F., Morais-Cabral J.H.
Activation of a nucleotide-dependent RCK domain requires binding of a cation cofactor to a conserved site. eLife8:, 2019. [Journal: Article] [CI: 11] [IF: 7,1]
DOI: 10.7554/eLife.50661 SCOPUS: 85077594921
Rocha R., Teixeira-Duarte C.M., Jorge J.M.P., Morais-Cabral J.H.
Characterization of the molecular properties of KtrC, a second RCK domain that regulates a Ktr channel in Bacillus subtilis. Journal of Structural Biology205(3):34-43, 2019. [Journal: Article] [CI: 22] [IF: 3,1]
DOI: 10.1016/j.jsb.2019.02.002 SCOPUS: 85061548530
Castro-Rodrigues A.F., Zhao Y., Fonseca F., Gabant G., Cadene M., Robertson G.A., Morais-Cabral J.H.
The Interaction between the Drosophila EAG Potassium Channel and the Protein Kinase CaMKII Involves an Extensive Interface at the Active Site of the Kinase. Journal of Molecular Biology430(24):5029-5049, 2018. [Journal: Article] [CI: 5] [IF: 5,1]
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.10.015 SCOPUS: 85056216681
Szollosi A., Vieira-Pires R., Teixeira-Duarte C., Rocha R., Morais-Cabral J.
Dissecting the Molecular Mechanism of Nucleotide-Dependent Activation of the KtrAB K+ Transporter. PLoS Biology14(1):, 2016. [Journal: Article] [CI: 22] [IF: 9,8]
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002356 SCOPUS: 84961353773
Harley C., Starek G., Jones D., Fernandes A., Robertson G., Morais-Cabral J.
Enhancement of hERG channel activity by scFv antibody fragments targeted to the PAS domain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America113(35):9916-9921, 2016. [Journal: Article] [CI: 17] [IF: 9,7]
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1601116113 SCOPUS: 84984876913
Marques-Carvalho M.J., Oppermann J., Muñoz E., Fernandes A.S., Gabant G., Cadene M., Heinemann S.H., Schönherr R., Morais-Cabral J.H.
Molecular Insights into the Mechanism of Calmodulin Inhibition of the EAG1 Potassium Channel. Structure24(10):1742-1754, 2016. [Journal: Article] [CI: 11] [IF: 4,9]
DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2016.07.020 SCOPUS: 84989908805