Bioengineered 3D Microenvironments
ABOUT
Our group focuses on the development of bioengineered microenvironments to promote controlled 3D cell assembly. We intend to recapitulate tissue-specific morphogenesis and differentiation, and understand the impact of microenvironmental signals on these processes. Ultimately, we aim to translate this knowledge into the design of advanced cell-delivery systems for regenerative therapies and 3D in vitro models.
RESEARCH
Engineering 3D cell morphogenesis
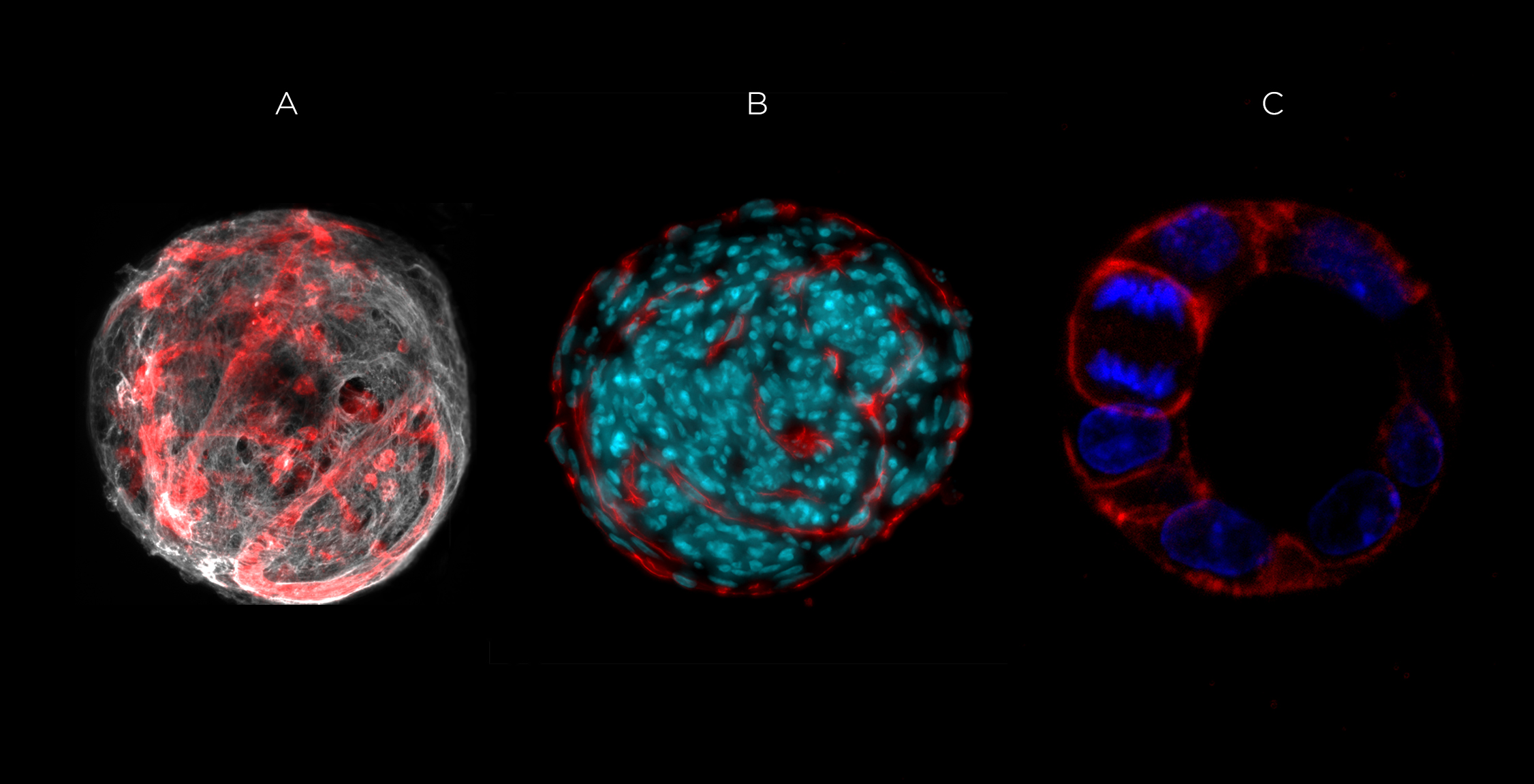
We have been developing cell-instructive hydrogels, ranging from complex multifunctional hydrogels, to “minimal matrices” containing only the essential biochemical/biomechanical signals for cells to exhibit their unique self-organizing properties and recapitulate tissue-specific morphogenesis and differentiation. By gaining insights into the mechanisms by which cells sense their microenvironment to organize into specific structures, and how this process can be guided by matrix features, we intend to advance the design of ECM-like 3D matrices for different therapeutic applications, from regenerative medicine to cancer.
Microarraying the cell microenvironment
In 3D microenvironments, cells respond to an array of soluble and matrix-associated cues and it is essential to systematically deconstruct their individual contribution and interplay. Yet, such combinatorial studies are very demanding. To address this challenge we are establishing high-throughput screening (HTS) platforms of 3D microarrays, where the combination of different cell-material scenarios into miniaturized specimens will allow assaying numerous variables in a time/cost-effective manner. In particular, it will greatly facilitate the testing of novel hydrogel formulations and optimization of 3D microenvironments.
Current research areas include:
- The development of pro-angiogenic scaffold-based and scaffold-free microtissues for cell-based regenerative therapy
- The development of 3D models to analyze the role of the ECM in cancer-related EMT (epithelial-to mesenchymal transitions)
Team
Selected Publications
Vascular units as advanced living materials for bottom-up engineering of perfusable 3D microvascular networks. Bioactive Materials38:499-511, 2024. [Journal: Article] [CI: 12] [IF: 20.3]
DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.05.021 SCOPUS: 85193041211
Barros da Silva P., Oliveira R.J.A., Araújo M., Caires H.R., Bidarra S.J., Barrias C.C.
An integrative alginate-based 3D in vitro model to explore epithelial-stromal cell dynamics in the breast tumor microenvironment. Carbohydrate Polymers342:, 2024. [Journal: Article] [CI: 9] [IF: 12.5]
DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.122363 SCOPUS: 85195551038
Carvalho E.D., Morais M.R.G., Pêgo A.P., Barrias C.C., Araújo M.
The interplay between chemical conjugation and biologic performance in the development of alginate-based 3D matrices to mimic neural microenvironments. Carbohydrate Polymers323:, 2024. [Journal: Article] [CI: 5] [IF: 12.5]
DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121412 SCOPUS: 85173151997
Magalhães M.V., Débera N., Pereira R.F., Neves M.I., Barrias C.C., Bidarra S.J.
In situ crosslinkable multi-functional and cell-responsive alginate 3D matrix via thiol-maleimide click chemistry. Carbohydrate Polymers337:, 2024. [Journal: Article] [CI: 15] [IF: 12.5]
DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.122144 SCOPUS: 85190291263
Neves M.I., Magalhães M.V., Bidarra S.J., Moroni L., Barrias C.C.
Versatile click alginate hydrogels with protease-sensitive domains as cell responsive/instructive 3D microenvironments. Carbohydrate Polymers320:, 2023. [Journal: Article] [CI: 15] [IF: 10.7]
DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121226 SCOPUS: 85165717522
Neves M.I., Bidarra S.J., Magalhães M.V., Torres A.L., Moroni L., Barrias C.C.
Microstructured click hydrogels for cell contact guidance in 3D. Materials Today Bio19:, 2023. [Journal: Article] [CI: 12] [IF: 8,2 (*)]
DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100604 SCOPUS: 85150054257
Feijão T., Neves M.I., Sousa A., Torres A.L., Bidarra S.J., Orge I.D., Carvalho D.T.O., Barrias C.C.
Engineering injectable vascularized tissues from the bottom-up: Dynamics of in-gel extra-spheroid dermal tissue assembly. Biomaterials279:, 2021. [Journal: Article] [CI: 17] [IF: 15,3]
DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121222 SCOPUS: 85118349708
Carvalho D.T.O., Feijão T., Neves M.I., Da Silva R.M.P., Barrias C.C.
Directed self-assembly of spheroids into modular vascular beds for engineering large tissue constructs. Biofabrication13(3):, 2021. [Journal: Article] [CI: 19] [IF: 11,1]
DOI: 10.1088/1758-5090/abc790 SCOPUS: 85105354294
Torres A.L., Bidarra S.J., Vasconcelos D.P., Barbosa J.N., Silva E.A., Nascimento D.S., Barrias C.C.
Microvascular engineering: Dynamic changes in microgel-entrapped vascular cells correlates with higher vasculogenic/angiogenic potential. Biomaterials228:, 2020. [Journal: Article] [CI: 40] [IF: 12,5]
DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119554 SCOPUS: 85074166551
Neves S.C., Moroni L., Barrias C.C., Granja P.L.
Leveling Up Hydrogels: Hybrid Systems in Tissue Engineering. Trends in Biotechnology38(3):292-315, 2020. [Journal: Review] [CI: 101] [IF: 19,5]
DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2019.09.004 SCOPUS: 85075891574
Torres A.L., Bidarra S.J., Pinto M.T., Aguiar P.C., Silva E.A., Barrias C.C.
Guiding morphogenesis in cell-instructive microgels for therapeutic angiogenesis. Biomaterials154:34-47, 2018. [Journal: Article] [CI: 52] [IF: 10,3]
DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.10.051 SCOPUS: 85032820887