Glycobiology in Cancer
ABOUT
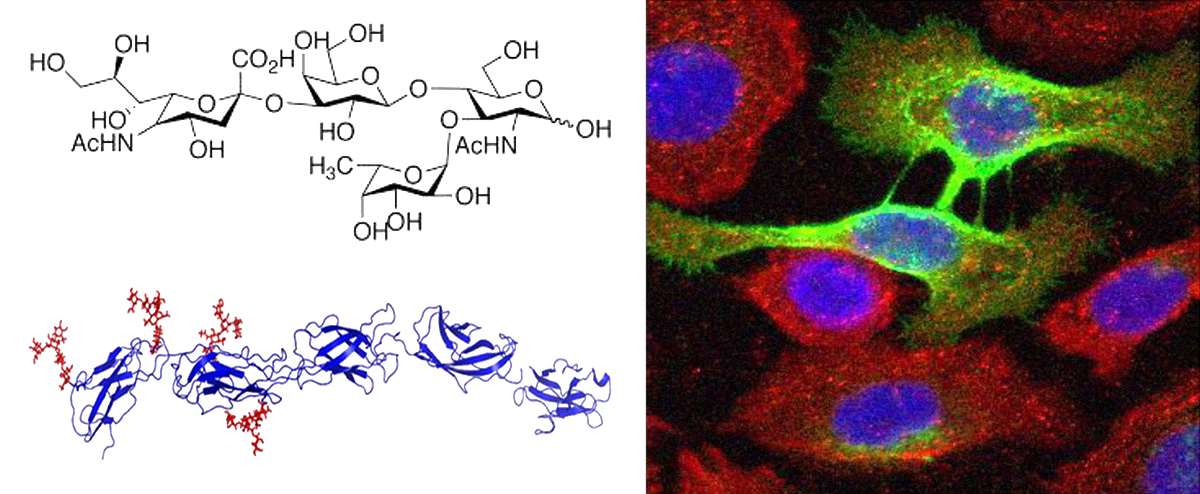
Glycans (carbohydrates, saccharide chains) are major components covering the surface of all living cells. Glycans are abundantly present in all membrane-associated and extracellular glycoconjugates (glycoproteins, proteoglycans and glycolipids). The cellular glycome provides a great diversity of molecular information on the cell surface and therefore is considered as the third language of life after the genome and the proteome.
The cellular glycome is produced by over 200 enzymes. Genetic and epigenetic alterations in the genes codifying these enzymes lead to defects in the glycome with major consequences in fundamental cellular processes and key functional impact in pathological conditions, as in cancer.
The Glycobiology in Cancer group addresses the role that glycosylation plays in cancer aiming at the understanding of the glycosylation-mediated molecular mechanisms controlling initiation, growth and progression of cancer. This provides the basis for the understanding of cancer therapy resistance and allows the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Moreover, we aim to understand the key role of cell surface glycans in the modulation of immune cells and the tumor microenvironment in order to target their therapeutic potential against cancer.
The Glycobiology in Cancer group main research projects are:
1) Evaluation of the role of glycans and glycan-binding proteins in cancer and pre-cancerous conditions addressing the molecular mechanisms controlling glycosylation of key molecules involved in cancer development and progression.
2) Understanding the biological function of glycans and glycoconjugates in cancer cell communication mediated by extracellular vesicles and its impact on cancer metastasis and tumor immunity, with the long-term goal of developing novel targets and improve cancer therapy.
3) Characterization of the glycosylation-mediated cancer therapy resistance to identify novel biomarkers for improved diagnosis, prognosis and patient stratification. This project provides molecular and functional data for novel cancer therapy targets and strategies.
4) Evaluation of the role of glycosylation-mediated immune modulation in cancer. Addressing the molecular, functional and clinical implications of glycans in tumor immunology in order to develop novel therapeutic strategies.
5) Characterization of the molecular mechanisms underlying the glycan-mediated host-pathogen crosstalk in chronic infection, inflammation and carcinogenesis.
The group applies multidisciplinary approaches with strong background in glycobiology and oncobiology combining advanced molecular and cell biology, together with biochemistry, genomics, glycomics, glycoproteomics, animal models and has access to large cancer clinical cohorts for understanding and addressing key mechanisms and functions played by glycosylation in cancer.
RESEARCH
We have identified specific sialylated glycan structures modulating the activity and biological function of several cellular proteins in cancer. We characterized the glycoproteome of tyrosine kinase receptors (HER2, EGFR, C-Met, RON), and other important players, including E-cadherin and CD44 in physiologic and pathologic conditions. We have further identified terminal alpha2,6 sialylation as an additional biomarker of cancer response to therapy, contributing to stratification of patients, which has potential implications in clinical decision-making in the context of gastrointestinal cancer. We have established an innovative workflow for extracellular vesicles (EVs) purification and glycosylation analysis in order to characterise the functional role of glycans, glycoproteins and proteoglycans in cancer-derived EVs from cell models and clinical samples.
We have disclosed mechanisms underlying glycosylation alterations in inflammation and their consequences in the context of pre-neoplastic lesions, such as Helicobacter pylori induced chronic inflammation and in the process of carcinogenesis and tumour progression. Our research has led to the identification of novel biomarkers with diagnostic and prognostic value and therapeutic targets, which are currently under pre-clinical and clinical evaluation.
Team
Selected Publications
ST6Gal1 targets the ectodomain of ErbB2 in a site-specific manner and regulates gastric cancer cell sensitivity to trastuzumab. Oncogene40(21):3719-3733, 2021. [Journal: Article] [CI: 50] [IF: 8,8]
DOI: 10.1038/s41388-021-01801-w SCOPUS: 85105357480
Marcos N.T., Pinho S., Grandela C., Cruz A., Samyn-Petit B., Harduin-Lepers A., Almeida R., Silva F., Morais V., Costa J., Kihlberg J., Clausen H., Reis C.A.
Role of the human ST6GalNAc-I and ST6GalNAc-II in the synthesis of the cancer-associated Sialyl-Tn antigen. Cancer Research64(19):7050-7057, 2004. [Journal: Article] [CI: 220] [IF: 7,7]
DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1921 SCOPUS: 4944265751
Rodrigues J.G., Duarte H.O., Gomes C., Balmaña M., Martins Á.M., Hensbergen P.J., de Ru A.H., Lima J., Albergaria A., van Veelen P.A., Wuhrer M., Gomes J., Reis C.A.
Terminal α2,6-sialylation of epidermal growth factor receptor modulates antibody therapy response of colorectal cancer cells. Cellular Oncology44(4):835-850, 2021. [Journal: Article] [CI: 31] [IF: 7,1]
DOI: 10.1007/s13402-021-00606-z SCOPUS: 85104515471
Magalhães A., Duarte H.O., Reis C.A.
Aberrant Glycosylation in Cancer: A Novel Molecular Mechanism Controlling Metastasis. Cancer Cell31(6):733-735, 2017. [Journal: Short Survey] [CI: 133] [IF: 22,8]
DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.05.012 SCOPUS: 85020642808
Freitas D., Campos D., Gomes J., Pinto F., Macedo J.A., Matos R., Mereiter S., Pinto M.T., Polónia A., Magalhães A., Reis C.A.
O-glycans truncation modulates gastric cancer cell signaling and transcription leading to a more aggressive phenotype. EBioMedicine40:349-362, 2019. [Journal: Article] [CI: 80] [IF: 5,7]
DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.01.017 SCOPUS: 85060115866
Poças J., Marques C., Gomes C., Otake A.H., Pinto F., Ferreira M., Silva T., Faria-Ramos I., Matos R., Ribeiro A.R., Senra E., Cavadas B., Batista S., Maia J., Macedo J.A., Lima L., Afonso L.P., Ferreira J.A., Santos L.L., Polónia A., Osório H., Belting M., Reis C.A., Costa-Silva B., Magalhães A.
Syndecan-4 is a maestro of gastric cancer cell invasion and communication that underscores poor survival. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America120(20):, 2023. [Journal: Article] [CI: 27] [IF: 9.4]
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2214853120 SCOPUS: 85158135443
Gomes J., Mereiter S., Magalhães A., Reis C.A.
Early GalNAc O-Glycosylation: Pushing the Tumor Boundaries. Cancer Cell32(5):544-545, 2017. [Journal: Short Survey] [CI: 15] [IF: 22,8]
DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.10.010 SCOPUS: 85033695819
Freitas D., Balmaña M., Poças J., Campos D., Osório H., Konstantinidi A., Vakhrushev S.Y., Magalhães A., Reis C.A.
Different isolation approaches lead to diverse glycosylated extracellular vesicle populations. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles8(1):, 2019. [Journal: Article] [CI: 88] [IF: 15]
DOI: 10.1080/20013078.2019.1621131 SCOPUS: 85074725417
Martins Á.M., Lopes T.M., Diniz F., Pires J., Osório H., Pinto F., Freitas D., Reis C.A.
Differential Protein and Glycan Packaging into Extracellular Vesicles in Response to 3D Gastric Cancer Cellular Organization. Advanced Science10(24):, 2023. [Journal: Article] [CI: 5] [IF: 15,1 (*)]
DOI: 10.1002/advs.202300588 SCOPUS: 85162202761
Zhang H., Freitas D., Kim H.S., Fabijanic K., Li Z., Chen H., Mark M.T., Molina H., Martin A.B., Bojmar L., Fang J., Rampersaud S., Hoshino A., Matei I., Kenific C.M., Nakajima M., Mutvei A.P., Sansone P., Buehring W., Wang H., Jimenez J.P., Cohen-Gould L., Paknejad N., Brendel M., Manova-Todorova K., Magalhães A., Ferreira J.A., Osório H., Silva A.M., Massey A., Cubillos-Ruiz J.R., Galletti G., Giannakakou P., Cuervo A.M., Blenis J., Schwartz R., Brady M.S., Peinado H., Bromberg J., Matsui H., Reis C.A., Lyden D.
Identification of distinct nanoparticles and subsets of extracellular vesicles by asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation. Nature Cell Biology20(3):332-343, 2018. [Journal: Article] [CI: 1390] [IF: 17,7]
DOI: 10.1038/s41556-018-0040-4 SCOPUS: 85042193942
Marcos N.T., Magalhães A., Ferreira B., Oliveira M.J., Carvalho A.S., Mendes N., Gilmartin T., Head S.R., Figueiredo C., David L., Santos-Silva F., Reis C.A.
Helicobacter pylori induces β3GnT5 in human gastric cell lines, modulating expression of the SabA ligand sialyl-Lewis x. Journal of Clinical Investigation118(6):2325-2336, 2008. [Journal: Article] [CI: 115] [IF: 16,6]
DOI: 10.1172/JCI34324 SCOPUS: 45649085812
Campos D., Freitas D., Gomes J., Magalhães A., Steentoft C., Gomes C., Vester-Christensen M.B., Ferreira J.A., Afonso L.P., Santos L.L., De Sousa J.P., Mandel U., Clausen H., Vakhrushev S.Y., Reis C.A.
Probing the O-glycoproteome of gastric cancer cell lines for biomarker discovery. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics14(6):1616-1629, 2015. [Journal: Article] [CI: 100] [IF: 5,9]
DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M114.046862 SCOPUS: 84930470850
Mereiter S., Balmaña M., Campos D., Gomes J., Reis C.A.
Glycosylation in the Era of Cancer-Targeted Therapy: Where Are We Heading?. Cancer Cell36(1):6-16, 2019. [Journal: Review] [CI: 441] [IF: 26,6]
DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.06.006 SCOPUS: 85067650826
Pinho S.S., Reis C.A.
Glycosylation in cancer: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Nature Reviews Cancer15(9):540-555, 2015. [Journal: Review] [CI: 2505] [IF: 34,2]
DOI: 10.1038/nrc3982 SCOPUS: 84940449986


